Topical pain relief creams, gels, and ointments are popular solutions for alleviating localized pain from conditions like arthritis, muscle strains, and minor injuries. While these products offer quick and effective relief, it’s crucial to understand the risks associated with their long-term use. This knowledge is essential for making informed decisions about managing pain and ensuring overall health and wellness.
- Potential Skin Irritation and Allergic Reactions
One of the immediate risks of prolonged use of topical pain relievers is skin irritation. Ingredients such as menthol, camphor, and methyl salicylate, commonly found in these products, can cause redness, itching, or even a burning sensation when used excessively. In some cases, individuals may develop allergic reactions, which can lead to more severe skin issues like dermatitis. Monitoring skin condition and discontinuing use at the first sign of adverse reactions is crucial.
- Systemic Absorption and Toxicity
Though designed for localized treatment, some active ingredients in topical pain relievers can be absorbed through the skin into the bloodstream. This systemic absorption can lead to toxicity, particularly if used in large quantities or over extended periods. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), commonly found in these products, can pose risks to the liver, kidneys, and gastrointestinal system when absorbed in significant amounts. Users should be cautious about the quantity and frequency of application.
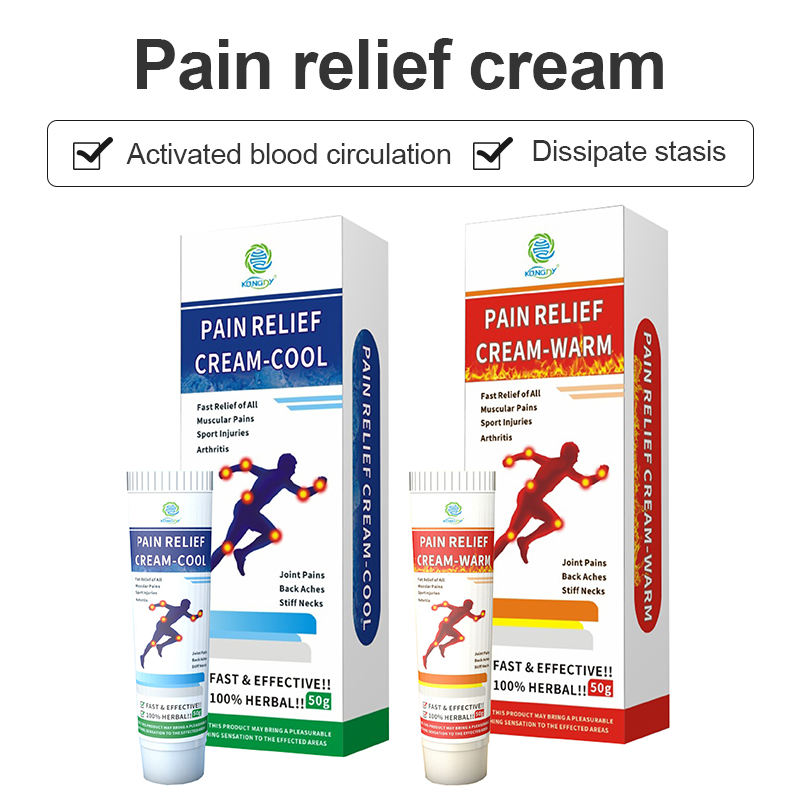
- Masking Underlying Conditions
Another significant risk is that relying on topical pain relief can mask symptoms of underlying health conditions. Pain is often a signal from the body indicating an issue that needs attention. By continually masking this pain with topical treatments, individuals may delay seeking appropriate medical evaluation and treatment, potentially allowing a condition to worsen. It’s essential to address the root cause of pain rather than just the symptom.
- Dependency and Overuse
Regular use of topical pain relievers can lead to dependency, where individuals feel they cannot manage their pain without these products. This dependency can result in overuse, increasing the risk of adverse effects and reducing the effectiveness of the treatment over time. A balanced approach that includes other pain management strategies, such as physical therapy, exercise, and proper medical treatment, is more sustainable and beneficial in the long run.
- Interaction with Other Medications
Topical pain relievers can interact with other medications, leading to reduced efficacy or increased risk of side effects. For instance, if you are using other NSAID-based medications orally, adding a topical NSAID can increase the risk of toxicity. Always consult with a healthcare professional before combining treatments to ensure safe and effective use.
Conclusion
While topical pain relief products can provide immediate comfort, it’s important to be aware of the risks associated with their long-term use. Skin irritation, systemic absorption, masking underlying conditions, dependency, and interactions with other medications are all potential concerns. For sustainable pain management, consider integrating a holistic approach that addresses the underlying causes of pain and includes a variety of treatments and lifestyle changes. Always consult with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive and safe pain management plan tailored to your needs.